
Framework for AI-Assisted Software Engineering
A modern software engineering methodology where AI is embedded into every stage of the lifecycle to increase efficiency, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market.

Framework for AI-Assisted Software Engineering
A modern software engineering methodology where AI is embedded into every stage of the lifecycle to increase efficiency, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market.
FASE outlines a modern software engineering methodology where AI is embedded into every stage of the lifecycle to increase efficiency, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market.
The framework empowers software designers, developers, and testers to achieve more in less time with higher consistency and quality. Its core principle is that human engineers focus on the "what" while AI handles much of the "how".
FASE extends well beyond code generation. It provides structured guidance across all key software engineering disciplines, including design, development, testing, and deployment. For each discipline, the framework defines recommended practices, tools, and measurable outcomes.
FASE is intentionally designed as a flexible framework rather than a rigid set of steps. Implementers are encouraged to create their own detailed implementation guides tailored to their specific organizational context.
The core principles that guide AI-Assisted software engineering excellence
Documentation is treated with the same importance as code, design, and testing. Well-structured and continuously updated documentation forms the foundation for effective AI-assisted development, enabling accurate code generation, better decision-making, and faster onboarding. By prioritizing documentation from the start, teams reduce ambiguity and ensure long-term maintainability.
AI can accelerate development, but responsibility always stays with humans. Engineers and product teams must validate, review, and approve every AI-generated artefact to ensure correctness, safety, and alignment with requirements. AI assists the process, but humans remain accountable for the final outcome and its real-world impact.
AI output is only as good as the input provided. Clear specifications, well-defined patterns, consistent guidelines, and accurate context lead to higher-quality AI-generated code, tests, and documentation. Investing in strong inputs through better prompts, better standards, and better context, directly improves the reliability and usefulness of AI outputs.
AI accelerates creation, but refinement and approval belong to humans. Across all phases of the lifecycle, from requirements to testing, humans validate AI outputs, refine them, and ensure they meet expectations. This collaborative loop ensures that speed does not compromise quality, and that the final product reflects both automation efficiency and human judgment.
AI adoption must result in tangible and trackable improvements. Teams should measure key metrics such as development speed, coverage, defect reduction, rework levels, and overall quality. By continuously monitoring outcomes and comparing them to historical baselines, organizations can validate the value of AI-assisted development and refine their approach to maximize impact.
The phase where ideas are transformed into a clear, structured software specification ready for implementation.
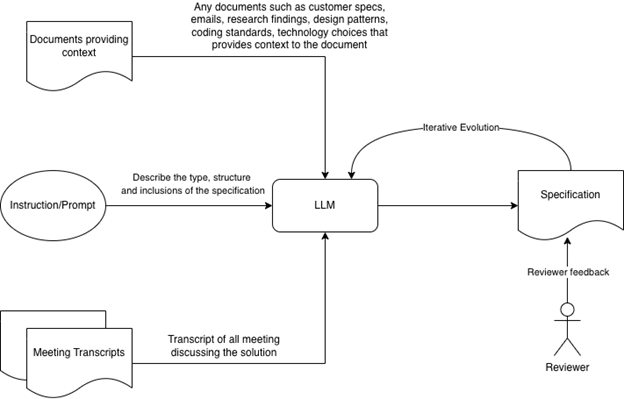
Meetings, workshops, and brainstorming sessions are where ideas are born. Recording these interactions creates a rich source of information that can be used to build accurate specifications.
AI tools can be extremely helpful in generating software specifications including BRS, SRS, design specifications, mind maps, and architecture diagrams.
Measures & Goals
Recommended Tools
With AI-Assisted code generation tools, rapid prototyping has become a reality. Even non-technical roles can build working prototypes and validate ideas quickly.
AI can significantly improve the speed and quality of code generation while maintaining careful planning and oversight.
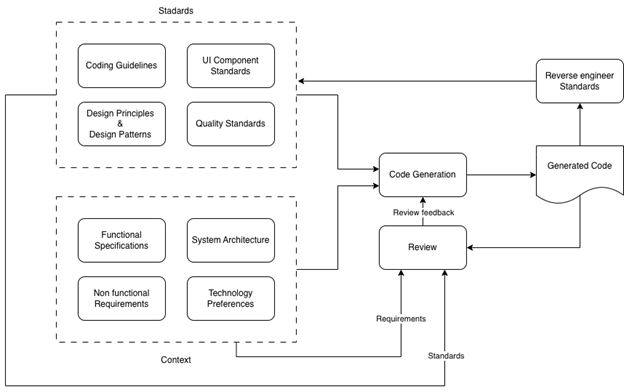
AI-accelerated development with proper standards
Measures & Goals
Meaningful tests for improved coverage
Measures & Goals
AI-assisted reviews for faster, consistent PRs
Measures & Goals
AI can greatly strengthen QA by generating comprehensive test cases, automating test scripts, and improving coverage across functional, API, performance, and load testing. With proper inputs and human oversight, AI can streamline QA workflows while maintaining high reliability.

AI can interpret functional specifications, user stories, and application flows to produce detailed test cases covering expected and edge scenarios.
Measures & Goals
AI can generate automated test scripts for UI, API, and integration testing based on the defined technology stack.
Measures & Goals
Understanding the limitations and challenges of AI-assisted software engineering
AI models can only process a limited amount of text at once. Large specifications, long code files, or complex documents may exceed this limit, requiring chunking or summarization to maintain accuracy.
Sensitive information such as source code, customer data, or internal documents cannot be shared with AI tools unless they operate within approved, secure environments. Proper controls must be in place.
AI may produce confident but incorrect or fabricated answers. Human review is essential to verify accuracy, prevent logical errors, and ensure outputs meet functional and quality expectations.
The quality of AI output is heavily influenced by the clarity and completeness of inputs such as specifications, prompts, and guidelines. Poor or incomplete inputs lead to weak or inaccurate results.
AI tools evolve rapidly. Model updates or version changes can alter behavior, output style, or accuracy, affecting reproducibility. Teams must be prepared to adapt prompts and workflows when models change.